Do you want to grow your investments beyond stocks and bonds? Gold derivatives could be the answer. These financial tools based on gold prices offer new chances.
This guide explains gold derivatives in simple terms. You’ll learn what they are, how they work, and if they fit your investment goals.
Read on to explore a different way to increase your wealth.
Gold Derivatives 101: Your Financial Superchargers
Gold derivatives are financial tools that let you bet on the price of gold without actually owning the metal. This might seem strange, but it’s an important idea to understand if you want to diversify your investments and manage risk.
What in the World Are Gold Derivatives?
Gold derivatives are contracts that get their value from the price of gold. They are different from owning physical gold or investing in gold ETFs, which mean you really have the metal.
With gold derivatives, you’re basically gambling on how the price of gold will move in the future. You can do this through different types of contracts, each with its own rules and level of difficulty.
Gold is a big market that can jump around due to lots of factors, like political events, what central banks do, and the state of the world economy. Understanding these things is key to making smart choices about gold derivatives.
Meet the Gold Derivative Family
Gold derivatives come in a few main types, and each one is good for different investment strategies. Let’s look at them:
Gold futures are standardized deals that trade on markets, obligating the buyer to buy or the seller to sell a certain amount of gold at a set price sometime in the future.
Futures are used a lot for hedging and guessing what will happen. They have high liquidity and leverage.
Gold options give the holder the right, but not the duty, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) the precious metal at a predetermined value before the end date. Options are handy for controlling risk and making money from price changes without putting up much cash.
Gold swaps involve trading cash based on the gold price. These are usually used by institutions to handle risk and liquidly.
Gold certificates are like playing cards that say you own gold stored by a financial place. While they let you invest in gold without having to hold onto the metal, the certificate’s worth is tied to the gold price.
Each type of gold derivative is different in terms of how complicated and easy to get into they are.
Futures and options are more standard and trade on markets, so they’re easier for individual investors to get into.
Swaps and certificates are often made up and used by institutions for special plans.
Understanding how these derivatives work with the rest of the gold market is crucial for coming up with a solid investment strategy.
For example, when the economy gets uncertain, gold derivatives often see more action as investors look for safe places to put their money.
By seeing these patterns, you can make better choices that go with your financial goals and how much risk you’re willing to take.
The idea of leverage in gold derivatives is also important to get.
Leverage lets you control a big amount of gold with a small investment, which can make your gains and losses bigger.
This means even small price swings can mean big wins or losses.
Gold Futures: Betting on Tomorrow’s Gold Price
Gold futures are a type of derivative that lets you make a guess about the future price of gold. They’re standardized contracts traded on exchanges like COMEX, and each contract typically represents 100 troy ounces of gold.
When you buy a futures contract, you’re agreeing to purchase this specified quantity of gold at an agreed-upon value on a future date.
How Gold Futures Work (And Why You Should Care)
The basics of buying and selling gold futures are quite straightforward.
You can buy or sell futures contracts through a brokerage firm or online trading platform.
The contract specifications, including size, delivery dates, and settlement methods, are standardized by the exchange.
For example, COMEX gold futures contracts have a minimum price movement of 10 cents per ounce, which equals $10 per contract.
Margin plays a big role in futures trading.
You’re required to deposit a margin, which is a part of the total contract value, to open a position. This allows you to control a larger notional value with a smaller amount of capital.
However, it’s essential to remember that leverage can make both gains and losses bigger.
Investors use gold futures for different reasons. Some use them to hedge against potential drops in gold prices, while others make guesses about price movements.
For instance, a gold mining company might use futures to lock in a selling price for their future production, protecting themselves against potential price drops.
The Good, the Bad, and the Risky of Gold Futures
Gold futures offer some good benefits.
Leverage allows you to manage a substantial gold position with a relatively small amount of money, making them a strong tool for portfolio diversification and hedging against inflation.
They can also be highly liquid, traded almost 24 hours a day, five days a week.
But these benefits come with some big risks. Market ups and downs can lead to big losses, especially due to leverage.
Margin calls can force you to put up more money to keep your positions, which can be hard on your finances.
The delivery day can also be a problem if you’re not ready for physical settlement.
The risk of the other party not fulfilling their end of the deal, known as counterparty risk, is lessened through the use of clearing houses, which make sure both sides of a futures contract keep their promises. This reduces the risk of one party not following through.
Knowing what’s going on in the market is important for futures trading.
You’ll often hear about “contango” and “backwardation.”
Contango indicates that the anticipated future value exceeds the current price, suggesting that investors think gold prices will go up.
Backwardation occurs when the expected future value falls below the current price, suggesting gold prices might go down.
It’s important to approach gold futures with care. They’re complex instruments that can result in substantial financial setbacks if not handled right.
Before jumping in, make sure you understand the basics, risks, and potential gains. Think about starting small and gradually increasing your involvement as you get more experience.
Gold futures can be a useful tool for protecting other investments. They can act as a hedge against inflation and currency shifts, and give you chances to make guesses about prices.
But remember, they’re not an investment you can just set up and forget. They need careful management and a good grasp of the market.
In terms of liquidity and standardization, gold futures have an advantage. They’re traded on established exchanges, and the contracts are standardized, making it easier to get in and out of positions.
But this also means they’re subject to market swings and can be affected by various factors, such as economic indicators, central bank actions, and global events.
Gold Options: Your Financial Insurance Policy
Gold options are powerful financial tools that give investors the flexibility to buy or sell gold at predetermined prices. These versatile tools serve two main purposes: protecting against market risks and guessing future price movements.
Understanding how gold options work is crucial for investors looking to diversify their portfolios and manage risk effectively.
Cracking the Code of Gold Options
Gold options come in two primary forms: call options and put options.
Call options allow the holder to purchase gold at a predetermined price (strike price) before the option expires, without imposing an obligation to do so.
Put options, conversely, grant the holder the ability to sell gold at the strike price before expiration, again without any requirement to exercise this right.
It’s important to know the difference between American-style and European-style options.
American options can be exercised at any time before they expire, offering more flexibility.
European options, however, can only be used at maturity.
Key terms to understand include:
- Strike Price: The price at which the option holder can buy or sell the underlying asset.
- Expiration Date: The date when the option contract expires.
- Premium: The cost of purchasing the option, influenced by factors such as volatility and time value.
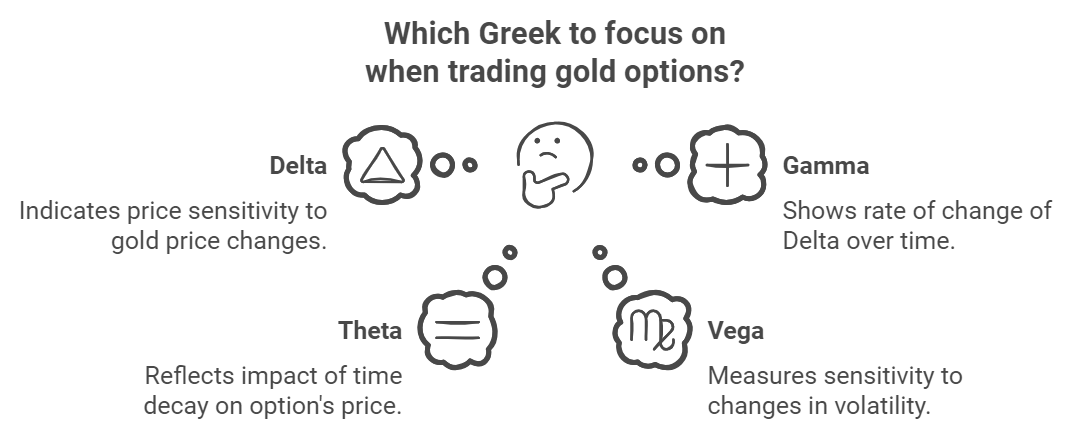
Options trading also involves understanding the “Greeks,” which measure different risk factors:
- Delta: Measures how much an option’s price is expected to change with a $1 move in gold’s price.
- Gamma: Shows the rate of change of Delta over time.
- Theta: Reflects the impact of time decay on the option’s price.
- Vega: Measures the option’s sensitivity to changes in volatility.
The Ups and Downs of Playing with Gold Options
Gold options offer several advantages for investors. They provide a way to protect a diversified portfolio, safeguarding against downturns in the gold market.
For instance, if an investor holds physical gold or gold mining stocks, they might buy put options to protect against potential price drops. This strategy limits possible losses while still allowing for upside potential.
Options also offer leverage, allowing investors to control a larger position without tying up significant funds. This can amplify potential returns, but it’s important to remember that it also increases risk.
However, options trading comes with its own challenges.
Time decay is a significant factor, as options lose value as they approach their expiration date.
This means that even if the price of gold doesn’t move, an option can lose value over time.
The volatility of gold prices can also greatly impact option pricing. Higher volatility usually leads to higher option premiums, reflecting the increased uncertainty in the market.
Despite these challenges, gold options offer unique benefits.
When buying options, the risk is limited to the premium paid, while the potential gains can be substantial if the market moves favorably.
This risk-reward profile makes options attractive for both protection and speculative purposes.
Common strategies include:
- Protective Puts: Buying a put option to protect against a potential drop in gold prices.
- Covered Calls: Selling a call option against a holding of physical gold or gold stocks to generate income.
- Bull Call Spreads: Buying a call option while simultaneously selling another call option with a higher strike price, reducing the cost of the trade while still allowing for potential profits.
It’s important to note that while buying options limits risk to the premium paid, selling options can expose investors to significant or even unlimited losses. Therefore, it’s crucial to understand the specific risks associated with each strategy before implementing it.
Gold options can be complex instruments that require a sound understanding of market dynamics and a willingness to actively monitor positions. However, with the right approach and knowledge, they can be an essential component of an investment strategy, providing both protection and growth potential in a well-diversified portfolio.
Gold Swaps and Certificates: The Road Less Traveled
When it comes to investing in gold, futures and options are often the top choices. However, gold swaps and certificates can also be interesting options for investors who want to diversify their portfolios.
These less common investment tools have their own advantages and challenges, making them worth considering for those who want to go beyond the usual paths.
Gold Swaps: Trading Gold Without Holding the Metal
Gold swaps are financial agreements that allow parties to exchange money based on gold’s market value.
These contracts come in two main types: fixed-for-floating and floating-for-fixed.
In a fixed-for-floating swap, one party pays a set rate while the other pays a rate that fluctuates with gold’s market performance.
The floating-for-fixed swap reverses these roles.
Institutional investors mainly use gold swaps to manage their exposure to gold prices without holding physical gold.
For example, a big financial institution might use a gold swap to protect against potential losses in their gold mining investments. If gold prices drop, the swap could offset some of those losses.
While gold swaps offer a lot of customization and flexibility, they’re generally more suitable for institutional investors or very sophisticated individuals due to their complexity. The over-the-counter (OTC) nature of these contracts means they’re not standardized like futures contracts, which can make them more difficult to understand and manage.
It’s important to understand that gold swaps come with significant counterparty risk. If the other party in the swap agreement defaults, you could face big losses.
This risk is one reason why gold swaps are typically the domain of large financial institutions with solid risk management systems.
Gold Certificates: Your Way into the Gold Market
Gold certificates offer a more straightforward way to invest in gold. These documents represent ownership of a specified quantity of the precious metal held by a financial institution.
They are primarily categorized into two distinct forms: allocated and unallocated.
Allocated certificates guarantee that specific gold bars are set aside in your name. It’s like having your name on a particular safety deposit box in a bank vault.
Unallocated certificates, on the other hand, represent a share in a larger pool of gold. Think of it as owning a portion of a gold mutual fund.
One of the primary advantages of gold certificates is their convenience. Unlike physical gold, which requires secure storage and insurance, certificates can be stored in a safe deposit box or even digitally.
This ease of storage often comes with lower fees compared to storing physical gold, making certificates an attractive option for investors who want exposure to gold without the hassle of holding bullion.
However, gold certificates aren’t without risks.
The most significant is counterparty risk – the chance that the issuer of the certificate might default or fail to deliver the underlying gold.
The 1933 Executive Order 6102 in the United States, which prohibited private gold ownership and required the surrender of gold certificates, serves as a historical reminder of how government actions can impact these investments.
When comparing gold certificates to other gold investment options, they offer a unique blend of convenience and flexibility. While they may not provide the same level of control as physical gold or the leverage of gold futures, they offer a means of gaining exposure to gold prices with a lower barrier to entry.
In the current regulatory environment, investors should be aware that gold certificates are subject to varying levels of oversight depending on the issuing institution and the jurisdiction. Always ensure you’re dealing with a reputable issuer and understand the terms and conditions of the certificate.
Gold Derivatives in Action: Performance When It Counts
Gold derivatives can be powerful tools, but their behavior isn’t always easy to predict. Let’s look at how these golden tools work when the market’s up and when it’s down.
How These Golden Tools Behave in Bull and Bear Markets
Gold derivatives have a special relationship with economic cycles.
When the economy is strong (a bull market), gold prices often rise because more gold is needed for industry and investors are more confident.
In a bear market, when the economy is weak, gold is often seen as a safe choice. This leads to higher demand and prices for gold.
But here’s where it gets interesting: gold derivatives are affected by more than just the price of gold.
These instruments can make gains or losses bigger. For example, if gold prices go up a lot due to economic uncertainty, gold futures and options might see even bigger movements because they let you buy with less money down.
A 5% increase in gold prices could mean a 20% or bigger increase in gold derivatives.
On the flip side, when gold is in a bear market, prices might drop sharply. Gold futures and options could fall even more, with some investors facing extra payments as their leveraged positions work against them.
It’s also worth looking at how gold derivatives compare to other investments, especially tech stocks.
While tech stocks can be very volatile, gold derivatives can be a steadying force in a diversified portfolio.
In general, they can help balance your investments.
What Makes Gold Derivative Prices Move
Now let’s get into what makes gold derivative prices change.
It’s not just about who’s buying or selling right now – even though those are big factors.
Interest rates, inflation, global events, and how people feel about the market all play a big role.
Interest rates and inflation are especially important.
When interest rates are low, it costs less to hold gold, making it more attractive. This can push up gold and gold derivative prices.
But if rates go up, gold becomes less appealing, so prices might fall.
Inflation is another key player. Gold frequently acts as a safeguard against eroding purchasing power, so when inflation goes up, gold prices often do too, helping derivatives.
But be careful – sometimes just the idea of inflation can make prices move more than actual inflation.
Global events can cause big swings in gold derivative prices. Political events, economic trouble, or major policy changes can trigger a surge in gold market activity.
The gold market, including both physical gold and derivatives, is very liquid with lots of daily trading.
Don’t forget about what central banks do. When they buy or sell gold, it can really influence the market.
What people think about gold (market sentiment) also matters a lot.
The gold market can be swayed by groupthink. If lots of people think gold will go up, prices do. If they think prices will fall, they do.
This effect is often stronger in the derivatives market because people can trade with less money.
Adding Gold Derivatives to Your Tech-Heavy Portfolio
Gold derivatives can be a very effective way to manage risk and increase potential returns. The key is to understand how gold derivatives work with your existing investments and to find the right balance between the two.
Balancing Act: Tech Stocks and Gold Derivatives
Tech stocks and gold often move in different directions. This makes gold derivatives a useful tool for spreading out your investments.
By adding gold derivatives, you can potentially reduce your portfolio’s ups and downs and make it more stable.
Consider the idea of how much your portfolio moves compared to the overall market.
Tech stocks often move a lot compared to the market. Gold, on the other hand, typically moves less.
By including gold derivatives in your portfolio, you might be able to smooth out some of those tech-related ups and downs.
But how much of your portfolio should you put into gold derivatives?
The answer depends on your appetite for financial uncertainty and your investment goals. Some investors prefer to start with a small amount, around 5-10%, and adjust as needed.
Others may choose to put a larger portion of their portfolio into gold derivatives.
Managing Risk Like a Pro
When it comes to managing risk in a portfolio that includes gold derivatives, there are several key strategies to keep in mind.
First, it’s essential to decide the optimal proportion of gold derivatives in your investment mix. This will depend on your risk tolerance and financial objectives.
Deciding how much to invest in each trade, also known as position sizing, is important when trading gold derivatives. By limiting your exposure to any single trade, you can reduce your potential losses and create a more sustainable investment strategy.
Stop-loss orders can be an effective tool for managing risk. These orders automatically sell your gold derivatives if they fall below a certain price, potentially limiting your losses.
Spreading your investments within your gold derivative holdings is also key. By putting your money into different types of gold derivatives, such as futures and options, you can minimize your vulnerability to any particular market or sector.
Options can be particularly useful for managing risk in futures positions. For example, buying put options on your gold futures contracts can provide a form of insurance against price drops.
It’s also important to regularly check on your portfolio and adjust your gold derivative positions as needed. By staying on top of market trends and economic indicators, you can make informed decisions about your investments and create a more effective risk management strategy.
Finally, think about stress testing your portfolio.
This involves simulating various market scenarios to see how your portfolio might perform. While it can’t predict the future, it can help you identify potential problems in your strategy.
Getting Started: Your Gold Derivative Roadmap
When you start trading gold derivatives, you need to pick a good broker and think about how taxes will affect your profits.
Choosing Your Gold Derivative Playground
You need to choose a reputable broker for trading gold derivatives. This choice is very important for your trading experience and investment safety. Here are some things to consider:
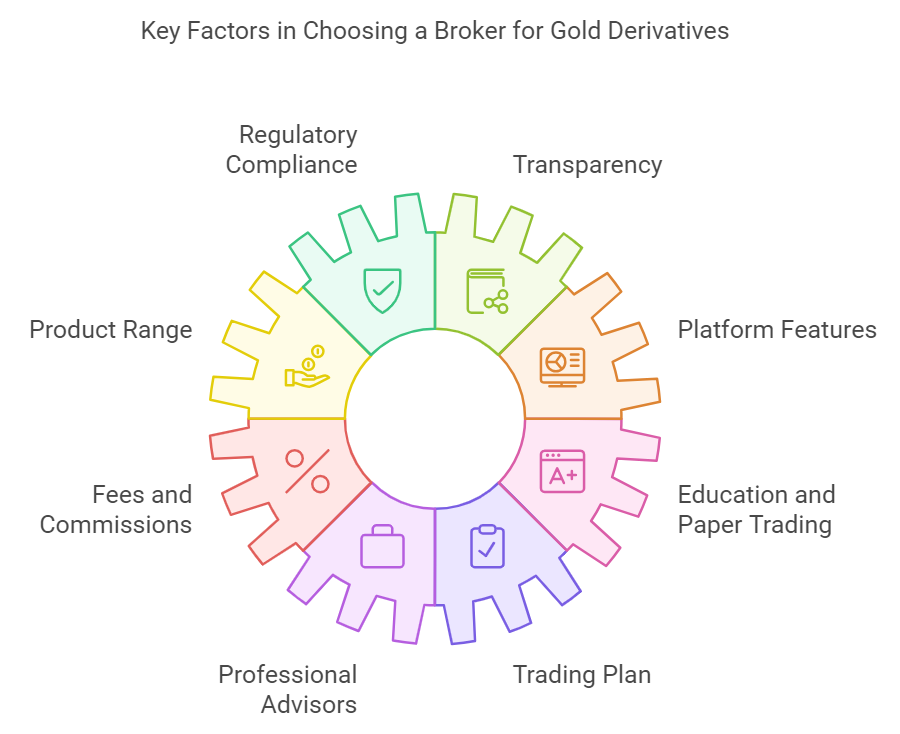
Regulatory Compliance: Look for brokers that are regulated by respected authorities like the SEC or CFTC in the United States. This ensures that there’s some oversight and protection for your investments.
Transparency: Find brokers that give you clear information about fees, trading conditions, and customer service quality.
Product Range: Check out the types of gold derivatives they offer. Some brokers specialize in certain derivatives like futures or options, while others offer a wider range.
Platform Features: A good trading platform is essential. Look for user-friendly interfaces, real-time data feeds, advanced charting tools, and comprehensive educational resources.
Fees and Commissions: Compare fees and commissions across different brokers. While it’s important to have competitive pricing, balance it with the quality of service and support.
Education and Paper Trading: Take advantage of educational resources and practice with paper trading or demo accounts. Many brokers offer these tools to help you improve your trading strategies.
Professional Advisors: Think about consulting with professional advisors who specialize in investment strategies. They can give you personalized advice based on your specific situation and trading activity.
Trading Plan: Develop a trading plan for gold derivatives. This plan should outline your goals, risk tolerance, and strategy for managing profits and losses.
Tax Talk: Uncle Sam’s Cut of Your Gold Profits
Taxes are a crucial part of trading gold derivatives that you need to understand.
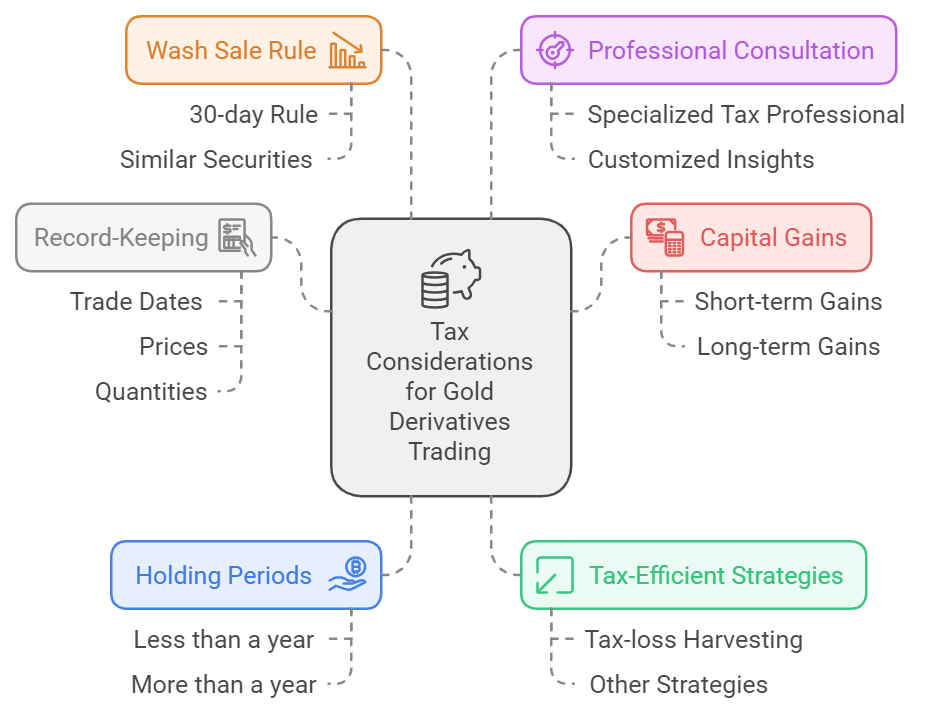
Capital Gains: Profits from gold derivative trading are usually subject to capital gains tax. The rate depends on how long you’ve held the investment and your overall income.
Holding Periods: Understand that the duration of your investment ownership impacts its tax treatment. Short-term gains (assets owned for less than a year) are usually taxed at your regular income rate, while long-term gains often have lower tax rates.
Strategies for Tax-Efficient Trading: Consider ways to lower your tax bill. Tax-loss harvesting can help you make the most of your investments by using losses to balance out gains.
The Wash Sale Rule: This rule stops you from claiming a loss on a security sale if you buy a very similar security within 30 days before or after the sale. Understand how this applies to your gold derivatives.
Professional Consultation: Given the complexity of tax laws, it’s a good idea to consult with a tax professional who specializes in investment taxes. They can offer insights customized to your particular circumstances and trading history.
Record-Keeping: Keep detailed records of all trades, including dates, prices, and quantities. Good record-keeping is important for accurate tax reporting and can be very helpful if you’re audited.
By choosing a good broker and understanding the tax implications of trading gold derivatives, you can have a smoother and more informed trading experience. This will let you focus on developing a trading plan and improving your investment strategies to maximize returns and minimize risks.
Final Remarks
Gold derivatives can enhance your tech-focused portfolio and protect it from market movements. Futures, options, swaps, and certificates each have upsides and downsides.
To start, learn about these investments and talk to a finance professional. Check out reliable brokers, know the tax guidelines, and consider putting a small amount of your capital into gold derivatives.
Your next move: choose one gold derivative type and dig into it deeply. This wise decision could help make your money safer long-term.











